WHAT IS ARTHRITIS?
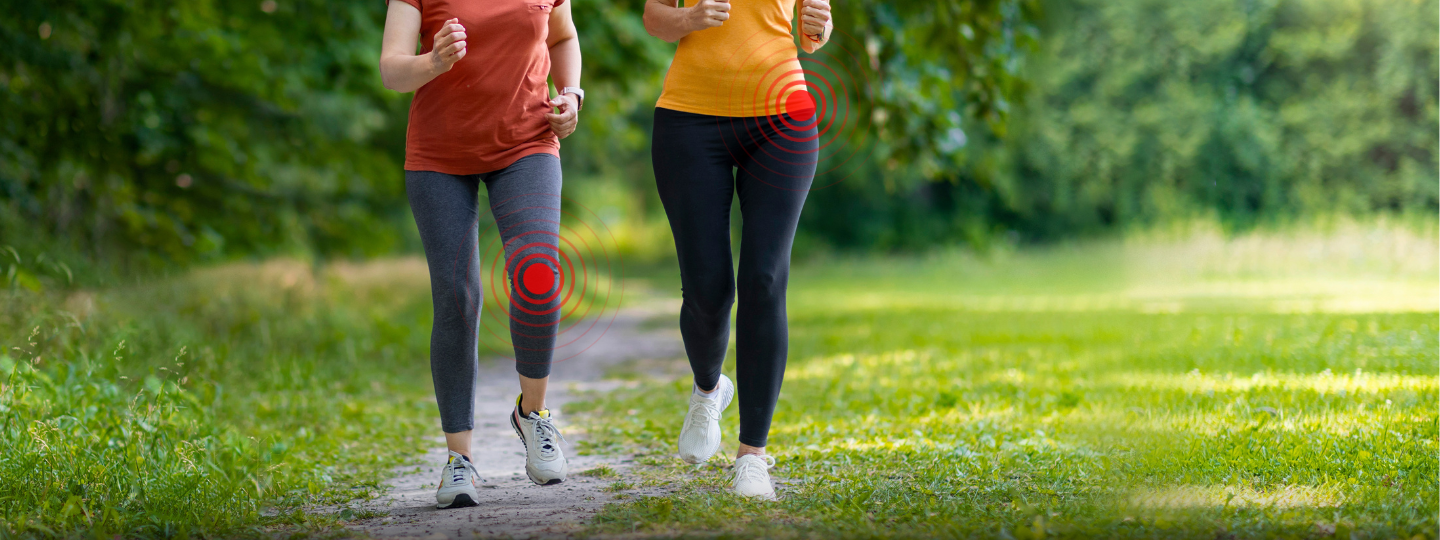
Degenerative joint disease or arthritis (also known as osteoarthritis) is a very common condition. It affects approximately 8.5 million people in the UK [Versus Arthritis]. It “can affect any joint in the body. It’s most likely to affect the joints that bear most of our weight, such as the knees and feet. Joints that we use a lot in everyday life, such as the joints of the hand, are also commonly affected” [Versus Arthritis]. Osteoarthritis is often thought of as ‘wear and tear’.
Osteoarthritis of the hip is also common and can affect either one or both hips. The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint which normally has a wide range of movement and bears a significant amount of body weight. In osteoarthritis, the joint becomes stiff and hurts when it is moved. Hip osteoarthritis is equally common in men and women [Versus Arthritis].
The problem occurs due to degeneration of the articular cartilage that lines the joint surface. In healthy joints, this surface provides a smooth gliding pain free range of motion. In arthritis, the cartilage becomes damaged. Fragments can break off causing inflammation in the joint. Pain can develop.
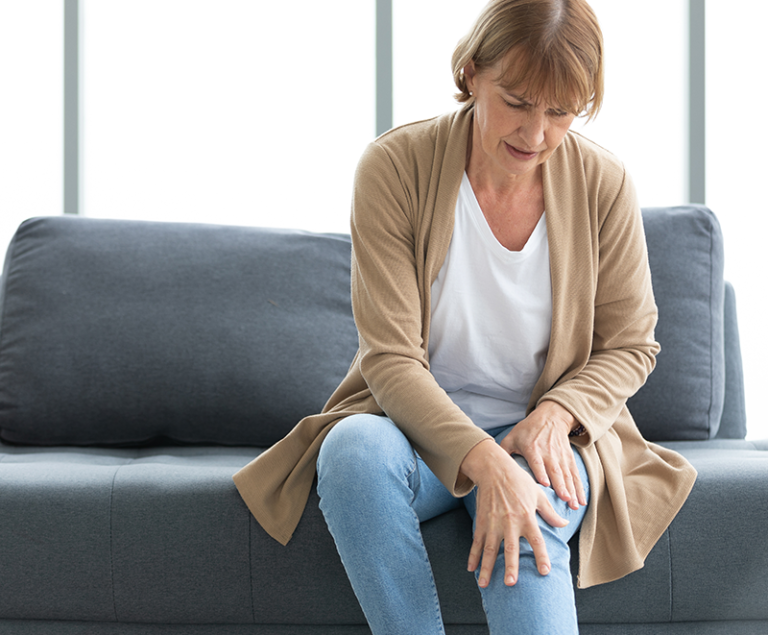
SYMPTOMS OF OSTEOARTHRITIS

RISK FACTORS
APPOINTMENTS & DIAGNOSIS
TREATING ARTHRITIS
Mr Vipin Asopa specialises in the treatment of degenerative arthritis or osteoarthritis. There are varying degrees of arthritis and therefore the treatment options will vary dependent on an individual and the level of pain they are experiencing. Treatment can be anything from not needing any immediate treatment to having knee replacement surgery. In most cases of early osteoarthritis, you won’t need to do anything. Other treatment options may include:
PAINKILLERS AND TOPICAL PREPERATIONS
Simple painkillers and topical preparations can help. Acupuncture and cold or heat compresses may also be beneficial.
MAINTAINING AN IDEAL BODYWEIGHT
Maintaining an ideal body weight can help with symptoms [https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/acr.24131].
ACTIVITY MODIFICATION
It could be the case that you are noticing particular activities are setting off your arthritis pain. This could be anything from playing sport, walking long distances or general chores around the house that are becoming increasingly difficult. Modifying these activities can help reduce the pain that is caused. For example, if running was affecting someone’s arthritis in the knee, they may decide that going for a more gentle jog or long distance walking is a better option for them to reduce the pain.
INJECTION THERAPY
When seeing a specialist, they may suggest the option of injection therapy. Different types of injection treatment exist. These include steroid injections, viscosupplementation and platelet rich plasma [https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/treatment/viscosupplementation-treatment-for-knee-arthritis/]. Some specialists also offer stem-cell based treatments. Careful scientific evaluation should be undertaken before considering this option [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36209438/].
PHYSIOTHERAPY
Your specialist may suggest physiotherapy, as this can help with strengthening the muscles and stabilising the ‘arthritic joint.’ Physiotherapy will not reverse degenerative change.
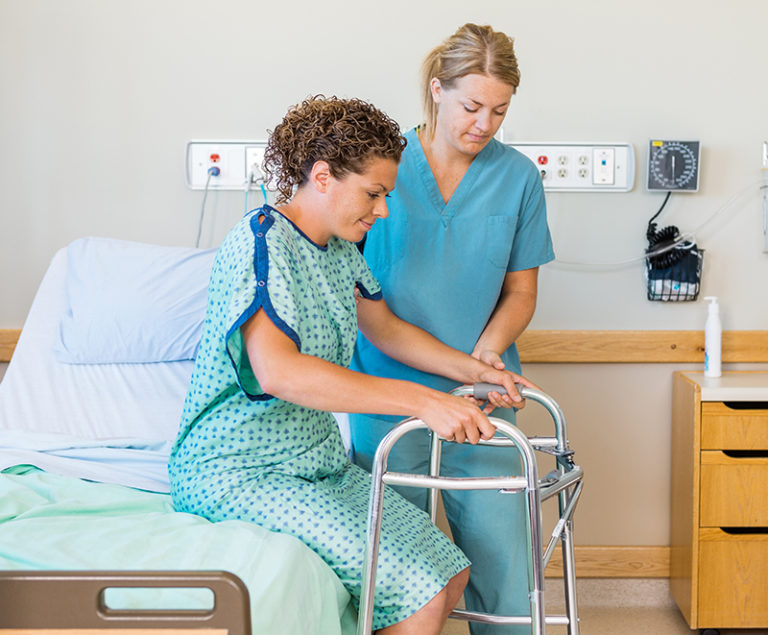
JOINT REPLACEMENT SURGERY
Knee/hip replacement surgery is considered when your quality of life is significantly limited by the arthritis and other treatment options have failed.
KNEE & HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY
Joint replacement is an effective treatment for arthritis. Your surgeon replaces the damaged surfaces with an artificial implant. With knee and hip arthritis, the joint surfaces break down causing pain and inflammation. Knee or hip replacement surgery is considered when your quality of life is significantly limited by the arthritis and other treatment options have failed. You may consider having joint replacement surgery if:
- You are experiencing significant pain
- You have pain that wakes you up at night
- A walking stick is needed to get around
- You are unable to perform many of your regular day to day activities
- It is affecting your quality of life and your ability to do the things that you would usually do.
Balancing the risks of surgery against this list of considerations may help you to decide whether you want to go ahead with a knee or hip replacement. The risks associated with knee and hip replacement surgery include infection, blood clots (DVT/PE), pain and stiffness, failure of operation, damage to nerves (leading to temporary or permanent numbness and weakness in the leg) and blood vessels injury. Death is a rare complication. A comprehensive review of complications related to knee surgery has been published here: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mporth.2019.10.004.
USEFUL INFORMATION
Book your Appointment
with Mr Vipin Asopa
To book an appointment or for any questions or information, please contact Mr Asopa's Medical Secretaries Mandy and Mary by phone or email:
Further information on osteoarthritis can be found on the National Institute of Clinical Excellence (NICE) website.
Acknowledgements
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Osteoarthritis.jpg
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/User:Homerstrykercenterlibrary
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/User:CFCF
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/User:Mikael_Häggström